Tinea Corporis
What is tinea corporis?
Tinea corporis is a superficial fungal infection of the skin that affects any region of the body, excluding the hands and feet, scalp, face and beard, groin, and nails. It is often known as ‘ringworm’ because of its distinctive ring-shaped lesions.
- Previous or concomitant tinea infections
- Diabetes mellitus
- Immunodeficiency
- Hyperhidrosis
- Xerosis
- Ichthyosis
- Hot, humid climates
- Household crowding
- Keeping house pets
- Recreational activities that include close contact with people.
Causes of tinea corporis
Tinea corporis is mostly caused by dermatophyte fungi of the genera Trichophyton and Microsporum .The most prevalent cause of tinea corporis is T. rubrum. It can also be caused by T. interdigitale, T. tonsurans, M. canis, T. verrucosum, T. equinum, and T. erinacei species. Infection can be acquired through direct skin contact with an infected person or animal, contact with fomites, or secondary dissemination from other sites of dermatophyte infection.
Clinical features of tinea corporis
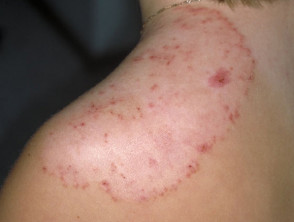
Tinea corporis first appears as a single circular red patch with a raised, scaly leading edge. A lesion spreads from the center to form a ring with central hypopigmentation and a scaly red rim (ringworm). The border may be papular or pustular. Itching is common. Multiple lesions can develop over time, which may lead to the formation of a polycyclic pattern. The distribution of lesions is often asymmetric.
Diagnosis of tinea corporis
Tinea corporis is usually diagnosed clinically after taking a complete history and physical examination. However, tests can be performed to confirm the diagnosis. Skin scrapings are examined under a microscope with KOH preparation, which will show branching, segmented hyphae. A fungal culture is another method to confirm the diagnosis. Tinea corporis is sometimes diagnosed with a skin biopsy.
Treatment for tinea corporis
General Measures:
The skin should be kept clean and completely dried. In hot and humid areas, loose-fitting, light clothes are recommended. Avoid close contact with infected people and the sharing of fomites.
Specific measures:
Topical antifungal treatments like imidazoles and terbinafine. It’s used to treat localized tinea corporis.
Oral antifungal treatment is often needed if tinea corporis affects a hair-bearing site, is widespread, or has not responded to topical antifungals. Terbinafine and itraconazole are the recommended oral antifungal medications.
Written by:
Atheer Alhuthaili , medical student.
Revised by:
Maee Barakeh , medical student.
References:
DermNet.
UpToDate.
Medscape.
Amboss.
