Flegel Disease
What is Flegel disease?
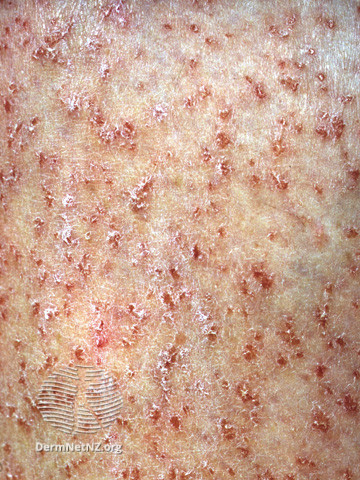
Flegel disease is often referred to as hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans. Flegel described for the first time in 1958. It is distinguished by red-brown papules with irregular, horny scales found primarily on the top surface of the feet and lower legs.
Causes of Flegel disease
The exact cause of the condition is uncertain. It is assumed to be a hereditary disorder.
It is assumed to be an inherited disorder, although the disease has been found in people with no family history. Sun exposure has also been linked, but not proven.
Clinical features of Flegel disease
Lesions are tiny, red-brown, scaly papules ranging in size from 1 to 5 mm that typically cover the surface of the foot and lower legs. When the scale is removed, a bright red base appears, typically with pinpoint bleeding. In rare cases, the outer ear lobes, arms, palms, soles, and oral mucosa may be impacted. The papules are usually painless.
Diagnosis of Flegel disease
Flegel disease is sometimes clinically diagnosed, particularly if there is a family history of the condition. Otherwise, a biopsy could reveal a pathological diagnosis of Flegel disease.
Treatment for Flegel disease
Lesions are benign and are primarily treated for cosmetic reasons. Treatment for Flegel illness includes:
– 5% fluorouracil cream was used topically for several months.
– Dermabrasion
– Cryotherapy
– Topical Retinoids
– Oral retinoid like isotretinoin or acitretin
Written by:
Atheer Alhuthaili , medical student.
References:
DermNet